Venomous Reptile Translocation Studies
 Translocation of Urban Gila Monsters: A Problematic Conservation Tool
Translocation of Urban Gila Monsters: A Problematic Conservation Tool
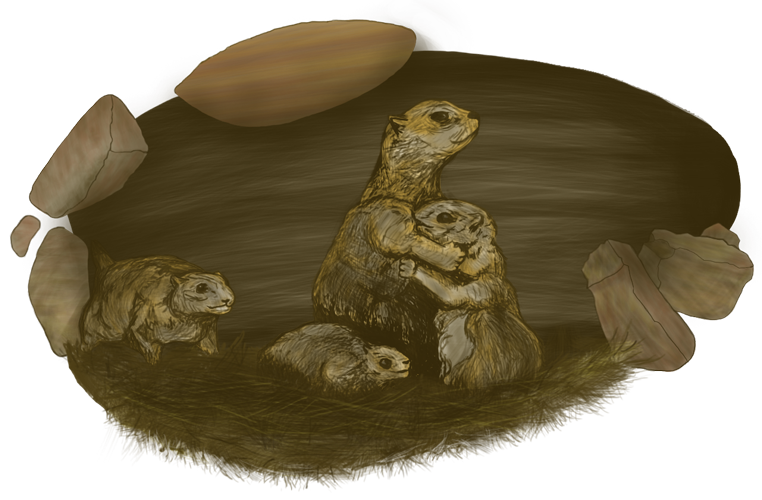
The Gila Monster (Heloderma suspectum) is a large, venomous lizard protected throughout its distribution in the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico. Rapid urban growth in key areas of its range and increased encounters with humans prompted us to investigate translocation as a conservation tool with ‘‘nuisance’’ Gila Monsters. Twenty-five Gila Monsters repor- ted as nuisances by residents in the northeastern Phoenix Metropolitan Area were translocated from 0 to 25,000 m from their point of capture. Subjects (N=18) translocated less than 1000 m returned to their original site of capture within 2–30 days; none of those (N=7) translocated more than 1000 m successfully returned, they exhibited high daily rates of speed, and were deprived the use of familiar refuges. We conclude that small distance translocations within suitable habitats are ineffective in removing Gila Monsters from areas deemed unsuitable. Moreover, individuals moved significantly greater distances are unlikely to remain at a translocation site, and may experience a variety of costs (e.g., predation risk) associated with high rates of movement.
# 2003 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Management of "Nuisance" Vipers: Effects of Translocation on Western Diamondback Rattlesnakes
by Erika M. Nowak, Trevor Hare, and Jude McNalley
A Message to Humans

"I used to be a city fellow. I grew up with the city noises of cars and trains and machines and humans. My family lived close to downtown Flagstaff not far from the railroad tracks along Route 66. What a busy, frightening place it was."
Read My Letter to You